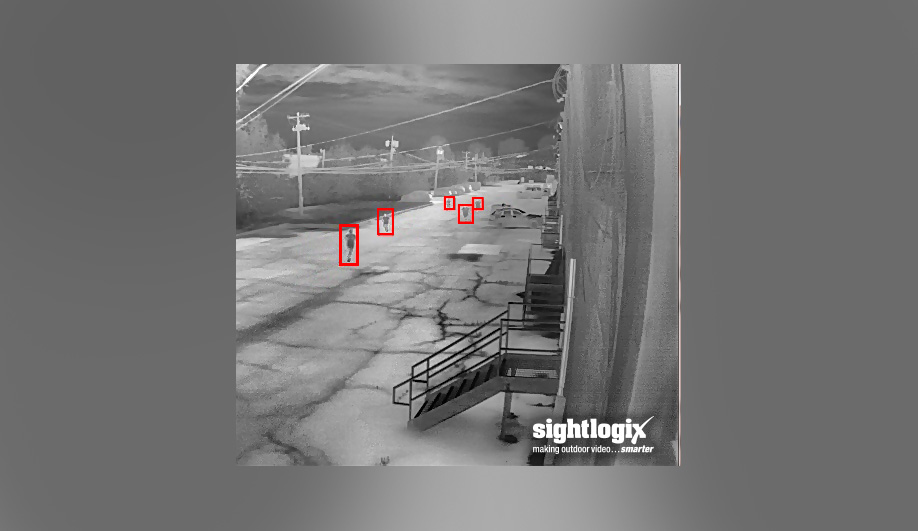
Safeguarding outdoor assets in a reliable and cost-effective manner often comes down to a single requirement: Accurate intruder alerts and timely information about the unfolding event. While there are many technologies available for outdoor security, smart cameras with video analytics have emerged as the solution of choice for detecting intruders in real time outdoors.
Yet the best technology will be handicapped if the alerts generated cannot be trusted. Repeated false alarms can eventually condition security operators to ignore real intrusions, undermining trust in the perimeter security system.
High Accuracy With Low False Alerts
In most cases the short-sighted response is to single out the security force as scapegoats, which ignores the real problem: alert fatigue. After responding to hundreds of perimeter breach alarms that turn out to be nothing more than small animals or windblown branches, even the most conscientious security guards lose confidence in the system and start to ignore its warnings.
There is no longer any reason for this situation to exist. By following best practices of product selection and deployment, it is now possible to use video security cameras to protect outdoor assets with high accuracy and low nuisance alerts.
As costs continue to fall, many |
Smart Thermal Cameras
Viable outdoor security must start with a sensing system that is accurate, 24-hours per day. For this reason, conventional wisdom asserts that smart thermal cameras are the best system for detecting intruders outdoors. This is because thermal cameras see heat rather than light, so they are a perfect “human detector,” and will ignore headlights, reflections off water, and other light-based activity, expanding their usefulness from their traditional role as night vision cameras to 24-hour intrusion detection solutions.
Smart thermal cameras with built-in Video Analytic software offers several advantages:
- They detect in the dark with no need for costly artificial lighting
- They work 24 hours/day
- They ignore reflections, shadows, moving headlights, direct sunlight, and other light-based phenomena that can trigger alarms in a visible camera detection system
- Because humans give off heat, thermal sensors are far more effective in spotting a person than visible cameras
- They detect body heat of intruders over large areas
In the past, the higher price for thermal technology limited their use in commercial applications, but as costs continue to fall, many organizations are now able to choose thermal cameras as the foundation for their outdoor detection applications.
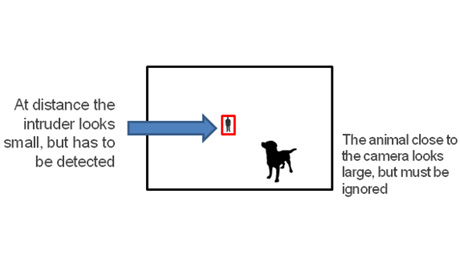 |
| A smart camera needs to ignore the animal while alerting on distant person, even though the animal will cover more of the camera’s field of view |
Accurate Detection With Geo-Registration
Smart thermal cameras are designed to detect movement, but outdoors, everything moves. A smart camera must be able to tell the difference between small objects such as leaves or debris and a person entering a secured area. One of the best ways for a camera to make this determination is through “geo-registration” which enables a three-dimensional capability. Geo-registration is a critical technology for accurate video analytic size rules that increase accuracy and reduce false alerts.
Consider how human vision works: Our eyes give us depth perception – we can tell which object is close and which is far. But a “one-eyed” camera can’t, unless it’s geo-registered. For example, a small animal near the camera will look much larger than a man at 300 meters away.
A smart camera needs to ignore the animal while alerting on distant person, even though the animal will cover more of the camera’s field of view.
Eliminate Camera Movement With Stabilisation
Many intrusion detection systems are deployed along open areas that are naturally impacted by high winds or vibrations from planes, trains, weather and machinery. Without image stabilisation, these applications can be overwhelmed by nuisance alarms or worse, outright misdetects. It is difficult for smart cameras to detect movement in a scene when the whole field of view is also moving from camera shake.
The best way to overcome the impact from wind or vibrations is to choose smart cameras that stabilise the image electronically, before the video analytic rules are applied. Look for cameras that use electronic or gyro-based stabilisers as a foundation for their detection capabilities.
Outdoor On-Board Video Analytics
Cameras which employ both a high degree of image processing and on-board video analytics have a great advantage in accuracy and detection distance over solutions that employ analytics on a server, outside of the camera.
Cameras without embedded analytics must compress the video data for transmission over the network. That’s a problem because compression removes most of the finer scene details—up to 99% of the original data—seriously degrading a video analytic system’s ability to accurately detect and recognize targets. In fact, on days with restricted visibility due to rain or fog, data compression has caused smart cameras to miss virtually all intruders in a scene.
On the other hand, when the uncompressed imagery is processed by video analytic software directly in the camera, 100% of the raw scene data is available for analysis. With on-board image processors examining the full visual detail of every video frame, you can achieve a much greater degree of accuracy in detecting motion and recognizing potential threats.
With on-board image processors |
Increasing Probability Of Detection
Smart thermal cameras are a great way to protect outdoor assets. But the system has little value if people can enter a secured area undetected. Here are some pointers to avoid gaps in coverage and make sure your system detects every time.
A perimeter security system based on video analytics operates by “seeing” targets that move into a camera’s detection area. Knowing the camera’s true range lets you design a dependable system with no coverage gaps.
Unfortunately, some manufacturers specify camera ranges that overstate their detection capabilities. This means it’s up to the integrator to determine the camera’s true detection distances. Otherwise your perimeter solution may leave gaping holes that can allow intruders to pass through undetected.
Determining True Detection Range
The best practice to determine a camera's true detection range is to measure the farthest distance at which the camera can automatically detect a person walking “inbound” or directly toward the camera. Inbound detection is always less than crossfield because a person moving across the camera's field of view creates a larger amount of motion, which is easier to detect. In contrast, a person walking toward the camera produces very little motion, making the target more difficult to detect. In the real world, intruders can enter a perimeter from any direction, so it’s important to design the system for all situations.
 |
| For complete coverage, the view of each camera must be designed to cover the adjacent camera’s blind spot |
Addressing Blind Spots
A camera’s field of view doesn’t begin where it’s mounted. Instead it can only detect at a measurable distance in front—this is the blind spot. Every security camera has a blind spot, and this must be considered in the perimeter security design, or someone will be able to walk right under a camera undetected.
To provide complete coverage, the view of each camera must be designed to cover the adjacent camera’s blind spot.
Perimeter Design Software
Some manufacturers offer design tools that can help you model a camera layout using a Google map of the area under consideration. This is a good practice to check detection distances ahead of time and ensure that blind spots are properly addressed. SightLogix offers such a tool, called SightSurvey.
Smart Video Solution
Today’s smart video is an ideal solution to the new challenges in site protection that confront security professionals. It outperforms older technologies by a wide margin. It often costs less. Installation is less disruptive, and the technology is highly reliable. Essentially, a smart video security system is a force multiplier, taking the burden of monotonous surveillance off regular security staff. Instead of just watching endless video feeds, the staff gets information that lets them do their jobs better. When deployed using best practices of product selection and installation, smart thermal video is the obvious choice for outdoor site security applications.
Learn why leading casinos are upgrading to smarter, faster, and more compliant systems