Counter surveillance
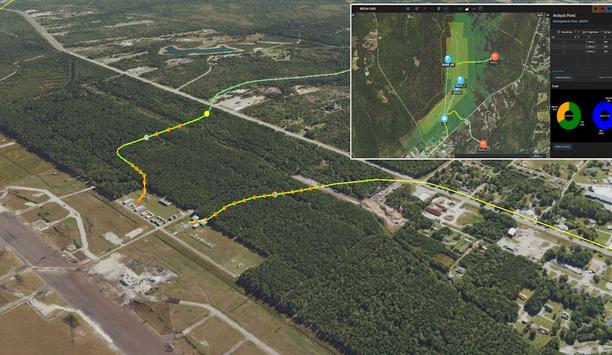
Omnisys introduces the BRO (Battle Resource Optimization) C-UAS system, a field-proven, real-time optimization platform built to help airport organizations mitigate the growing threat of unauthorized and hostile unmanned aerial systems (UAS). The system enables data-driven, proportionate responses to aerial threats, ensuring passenger safety while maintaining airport operations. In recent months, airports across Europe and the US have faced repeated shutdowns due to unauthorized drone...
DeterTech, a major innovator of risk management and crime prevention solutions, has donated £5,000 to National Crimebeat, a youth-focused charity that supports community-led crime reduction initiatives across the UK. National Crimebeat is passionate about empowering the next generation and DeterTech’s donation will aid the charity in continuing to support young people across the UK, rewarding a broad range of initiatives led by young people to reduce crime. National Crimebeat...
Sentrycs, a global pioneer in Protocol Manipulation-based counter-drone technology—commonly known as Cyber over RF, and Omnisys, a global expert in mission optimization for defense and homeland security, have announced a strategic collaboration that combines their technologies to improve the planning and deployment of sensor systems in multi-domain operations. The joint solution merges Sentrycs’ field-proven C-UAS systems with Omnisys’ BRO-AD (Battle Resource Optimization for...
Just a few months after the release of RDID 1.0, Spotter Global is proud to announce the release of RDID 2.0. This sensor is for detecting and tracking FAA-compliant Wifi and Bluetooth drones as well as their pilots. Upholding the Spotter Global motto, “First to Detect, First to Protect™”, RDID 2.0 will empower law enforcement and security personnel with a cost-effective solution to reliably detect 90+% of drones in their airspace, with zero false alarms and swiftly reach the...
At a hearing on Sept. 16, 2025, Brett Feddersen, Chair of the Security Industry Association (SIA) Drone Security Subcommittee and vice president for strategy and government affairs at D-Fend Solutions, testified before members of Congress to discuss increasing risks from the misuse use of drones and give legislative recommendations for implementing a clear and comprehensive framework for the use of counterdrone technologies and operations across the United States. The hearing — “Unm...
DeterTech invites industry professionals to the official launch of its newly constructed BS EN 50518:2019 Category 1 Alarm Receiving Center (ARC) in Prestwick on Wednesday, 8th October. The day will be packed full of live demos, exclusive behind-the-scenes tours, and unique insights from experts across the crime intelligence and site security community. Speakers will include Detective Inspector Lawrence Billi of OPAL, the national police intelligence unit for serious organiz...
News
Kibo, a major manufacturer of modular bulletproof structures, and Sentrycs, a global innovator in counter-drone (C-UAS) solutions, announce a collaboration that delivers a fully integrated, mission-ready security platform designed to counter both ground and aerial threats. As threats continue to evolve, ranging from physical attacks to drone-based surveillance and smuggling, security and defense forces worldwide are seeking fast-to-deploy, versatile solutions that ensure comprehensive protection. The Kibo–Sentrycs integrated platform answers this need with a plug-and-play mobile system that combines field-proven infrastructure with advanced aerial threat defense in a single, unified solution. Kibo’s bulletproof modular structures It streamlines deployment, reduces personnel and logistical demands, and delivers full-spectrum protection against both ground and airborne threats. The integrated solution combines Kibo’s bulletproof modular structures, already used by military, police The integrated solution combines Kibo’s bulletproof modular structures, already used by military, police, and critical infrastructure operators, with Sentrycs’ autonomous counter-drone system, which is operational in over 20 countries across six continents. The result is a preconfigured platform that can be used as a tactical command post, checkpoint, border control unit, or mobile surveillance station, equipped to detect, identify, track, and mitigate unauthorized drones easily and effectively with no collateral damage. Security environments Designed for strategic mobility, the system can be quickly relocated to match changing threat environments, making it ideal for border crossings, base perimeters, and temporary deployments. “Today’s security environments demand agility, precision, and the ability to defend against various threats across multiple vectors simultaneously,” said George Glentos, Founder and CEO of Kibo, adding “To address this need, we combined two field-proven technologies and developed an integrated platform that simplifies deployment, enhances protection, and delivers operational advantage.” RFC-UAS system “Integrating Sentrycs’ Cyber over RFC-UAS system into Kibo’s mobile, bulletproof structures delivers a unique combination of advanced drone defense and physical protection,” said Meir Avidan, VP Business Development and Strategic Partnerships at Sentrycs, adding “It serves as a force multiplier for missions requiring speed, reliability, and multidomain readiness, providing security forces with both tactical flexibility and enhanced protection.” The collaboration was initiated and facilitated by NextNow, a strategic consulting firm that connects innovative security technologies with operational needs across the defense and homeland security ecosystem, led by Major General (ret.) Alon Levavi.
UVision Air Ltd., a global pioneer in loitering munition systems, is unveiling a major advancement in autonomous warfare: an AI-based Common Operating System (COS) that serves as a unified platform for operating multiple loitering munitions of various classes, mission types, and deployment levels. Designed for full interoperability, the COS enables seamless integration of rotary-wing platforms, such as the Viper system by SpearUAV – operated at tactical team levels including squad, platoon, battalion, and beyond – alongside Uvision’s fixed-wing HERO family, including the long-range, high-payload HERO-120 and HERO-400. The result is a truly heterogeneous ecosystem, all operating under a single AI-powered control layer. Real-time adaptability to evolving threats At the core of the system is a multi-layered AI engine that autonomously manages complex mission execution At the core of the system is a multi-layered AI engine that autonomously manages complex mission execution across a heterogeneous array of assets. Tasks are intelligently allocated: one munition may penetrate and disrupt electronic warfare defenses, another performs ISR and real-time target acquisition, and a third executes a coordinated precision strike. This mission-centric distribution ensures real-time adaptability to evolving threats, delivering both terrain dominance and operational superiority. Command-and-control ecosystems The COS performs continuous optimization based on target profile, terrain, and platform availability, maximizing effect, while minimizing resource expenditure. This allows commanders to make data-driven decisions on how many and which types of munitions to deploy for maximum mission effectiveness and cost-efficiency. With an open-architecture design, UVision’s COS integrates seamlessly into existing command-and-control ecosystems, reducing barriers to adoption and enhancing cross-platform synergy. New Common Operating System Dr. Ran Gozali, CEO of UVision Air Ltd., stated: "This new Common Operating System transforms loitering munitions into a smart, coordinated system-of-systems. It reflects UVision’s strategic shift toward integrated, modular combat solutions that are both operationally decisive and cost-effective." Dr. Ran Gozali adds, "Forces no longer need to expend high-end weapons for every target. Instead, they can deploy the right capability for each mission and dominate the battlespace with agility and intelligence."
Sentinel Photonics, a pioneering innovator in laser detection and protection technologies, announces ECHO and LASERD® MAX, two new laser detection capabilities designed to expose covert threats and give operators a critical edge in laser-contested environments. Both will be shown for the first time at DSEI, Excel London, 9 - 12 September 2025, Stand N5-260. Real-time laser intelligence “Laser threats are evolving fast, creating serious multi-domain risks that traditional defenses can’t keep up with,” says Jackson White, Head of Commercial at Sentinel Photonics. “Our new products are built to detect those threats early and help save lives. ECHO reveals surveillance optics that others are trying to hide, quickly and safely. LASERD MAX goes beyond detection. It gives operators real-time laser intelligence they can act on to enhance their survivability.” ECHO: Handheld retro-reflective detection for covert optics ECHO uses advanced retro-reflection to uncover surveillance threats that conventional imaging systems miss ECHO is a rugged handheld laser detection system that exposes concealed, hostile optics, specifically magnified optics of any kind. Designed for military, law enforcement and high-security operations, ECHO can detect optics at distances of up to 3 km, even under harsh environmental conditions with speed and precision. ECHO uses advanced retro-reflection to uncover surveillance threats that conventional imaging systems miss. It operates across the wide spectrum, allowing operators to identify concealed optics without compromising their own position, giving them the edge in surveillance, counter-surveillance, VIP protection, sniper scope detection, and border operations, while remaining eyes safe. ECHO at a glance: Handheld retro-reflective detection of optics: Gives the ability to identify covert and low-profile optics Operates across a wide band: Operates in the VIS, NIR and SWIR bands Long-range capability: 50 m to 3 km detection range Covert and secure: Low visibility to NV and low-light cameras Eye safe operation: Can be used with no or very little training while being completely eye safe Visual intel on demand: Onboard screen, video capture, and sharing LASERD® MAX: era of laser intelligence and threat detection LasINT system that gives operators real-time situational awareness of unknown laser threats Sentinel also officially releases LASERD® MAX, its advanced Laser Intelligence (LasINT) system that gives operators real-time situational awareness of unknown laser threats. Designed for high-tempo, high-threat operations, LASERD® MAX delivers persistent, autonomous laser detection up to 10km across the visible and non-visible laser spectrum. It enables users to passively map, log, and analyze laser activity in real time, even in complex or contested EW environments. Threat types include LDEWs, rangefinders, beamriders, LIDAR, covert illuminators, and more. With a compact footprint and multiple camouflage options, LASERD® MAX is field-ready for land, sea, and air platforms. LASERD MAX at a glance Autonomous passive scanning: Real-time spectral analysis of the battlespace with auto-updating threat parameters Simultaneous multi-threat tracking: Parallel detection of military-grade and commercial laser sources across wide-area coverage, with a 10 km-range High-fidelity capture engine: Captures transient, low-signature laser events using class-leading photodetectors with high pulse sensitivity (10pJcm²) LasINT data architecture: Builds a bespoke laser threat library to inform strategic and tactical responses and integrates seamlessly with C4ISR ecosystems Remote and standalone deployment: Fully networkable via secure protocols or operable independently in the field. ECHO is available now. LASERD MAX is available now. ECHO and LASERD MAX will be demonstrated for the first time at DSEI, Excel London, 9 - 12 September 2025, Stand N5-260.
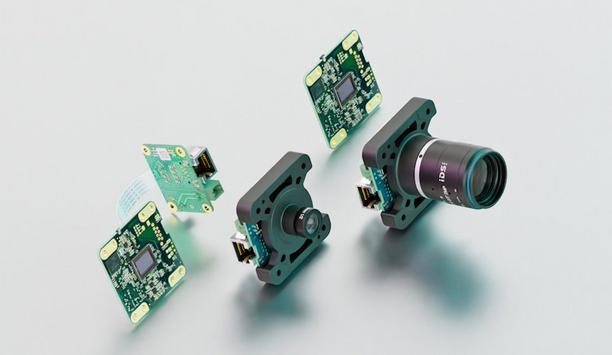
Whether in quality assurance, medical technology or automation - industrial image processing places high demands on precision and reliability, even under difficult conditions. IDS Imaging Development Systems GmbH is therefore expanding its portfolio of cost-optimized project cameras from the GigE uEye LE series with state-of-the-art Sony Starvis 2 sensors from the end of June 2025. These deliver impressive image quality even in low ambient light. The new single-board cameras are GigE Vision-compliant, space-saving and designed for high-volume applications. Great price-performance ratio The 12.5 megapixel version with its square 1/1.6" sensor is ideal for use in microscopy applications Thanks to their attractive price-performance ratio, they are suitable for cost-critical industrial projects. With the IMX675 (5 MP), IMX676 (12.5 MP) and IMX678 (8 MP) sensor variants, IDS will soon be able to offer further high-performance options for a wide range of requirements. The 12.5 megapixel version with its square 1/1.6" sensor is ideal for use in microscopy applications, for example. The Sony Starvis 2 sensors utilize the latest CMOS technology, which impresses with excellent light sensitivity, low noise and an extended dynamic range. They were developed for applications where the highest image quality is required and guarantee detailed pictures even in difficult lighting conditions. Made in Germany The introduction of the new models strengthens IDS's position as a supplier of versatile, powerful and economical image processing components - "Made in Germany". Like all members of the GigE uEye LE family, they follow the design-to-cost principle and are aimed specifically at users who want to efficiently integrate camera technology into machines, devices or embedded systems.
ZKTeco USA, a major provider of biometric verification and access control technology, announced the company has launched its new cloud-based access control software platform, Cielo365 that is changing the game in access control. Cielo365 is an add-on product that enables customers to easily transition from an on-premise solution to a cloud-based system effortlessly. The new software supports legacy ZKTeco devices and is compatible with existing access control hardware including SpeedFace and Pro Series panels, and new hardware such as the Omni Series. Cielo365 Cielo365 is an industry pioneer, cloud-based SaaS access control software application that allows users the ability to manage their access control from anywhere at any time, on any device. “We truly offer customers a one stop shop access control solution that is extremely scalable and cost effective,” states Esteban Pastor from ZKTeco USA. “Users now have an easy way to transition to the cloud with Cielo365 and utilize one centralized interface to control access and monitor multiple locations globally.” Blue Sky and ZKTeco partnership “Blue Sky Systems is extremely excited to partner with ZKTeco USA and provide greater choice to customers looking for a cloud solution,” states Jason Bair. “The best part about Cielo365 is the ease of integration to ZKTeco’s existing standalone reader & controller; making it the perfect solution for customers who want to transition to the cloud with ease." Software features Cielo365 software was designed to be a flexible, scalable foundation to help customers elevate their security Cielo365 software was designed to be a flexible, scalable foundation to help customers elevate their security by eliminating the need for onsite servers. Features include device and real-time monitoring, alarms & notifications, multi-site management, site maps and reports, customer user roles, and interlock & anti-passback. With remote access capabilities, users receive their own login and can manage various functions, such as opening doors, locking doors, adding users, and more, from any location using their tablet, laptop, home PC, or mobile device. Needs of the market ZKTeco USA understands the needs of the market and manufactures all products in-house to help keep costs low and quality high. Its rugged hardware line includes a standalone reader and controller that eliminates the need for wires for a faster installation. With different screen sizes available, the standalone unit can be used as an intercom and integrated with visitor management, biometrics & video surveillance systems, and can also be used for mobile credential management. ZKTeco USA offers everything needed to streamline an organization's access control, whether it’s across a single facility or multiple sites.
Sentrycs, a technology major in Protocol Manipulation-based counter-UAS solutions, has been named one of the top global innovators and growth leaders in Frost & Sullivan’s Frost Radar: UAS Communication Disruptors, 2025. This prestigious recognition highlights Sentrycs’ position at the forefront of the counter-drone industry and reflects its rapid growth, continuous innovation, and field-proven capabilities. Frost & Sullivan’s Frost Radar Frost & Sullivan’s Frost Radar identifies the world’s most impactful firms disrupting drone communications Frost & Sullivan’s Frost Radar identifies the world’s most impactful companies disrupting drone communications, benchmarking them based on their innovation strategies, growth performance, and ability to deliver real-world results. Sentrycs stood out in both Innovation and Growth indices for its unique approach to drone threat mitigation, robust global traction, and next-generation technology. Sentrycs’ advanced counter-drone solution According to the report, Sentrycs’ advanced counter-drone solution leverages Protocol Manipulation (often referred to as Cyber over RF) to detect, track, identify, and neutralize unauthorized Group 1 and Group 2 drones, including coordinated swarms and elusive DIY drones that evade traditional detection. Its technology enables authorities to mitigate threats with minimal collateral damage using features such as Smart Disconnect and safe, pre-programmed landings. Sentrycs HORIZON The launch of Sentrycs HORIZON in early 2025 further strengthened the company’s capabilities The launch of Sentrycs HORIZON in early 2025 further strengthened the company’s capabilities, introducing an AI-powered functionality that continuously analyses the radio-frequency environment and adapts to unknown signals in real-time without relying on pre-existing libraries. In addition to technological innovation, the company has demonstrated outstanding business performance, quadrupling its size in 2024 and securing major deals across 6 continents. Its recent deployments include the protection of military bases, national defense projects, and law enforcement operations, with an increasing footprint in over 20 countries worldwide. Smart, non-intrusive counter-drone technology “This recognition by Frost & Sullivan is a powerful validation of our mission to make the world safer through smarter, non-intrusive counter-drone technology,” said Jason Moore, CRO of Sentrycs, adding “As drone threats continue to evolve, we remain committed to delivering solutions that combine cutting-edge innovation with operational simplicity, reliability, and affordability.” “Sentrycs is one of the top companies in the counter-UAS space, firmly establishing itself as one of the pioneers for its cyber-RF capabilities.” noted Tobias Folatelli, Research Analyst at Frost & Sullivan. Sentrycs well-positioned for continued growth Folatelli further emphasized that Sentrycs is well-positioned for continued growth, with further expansion opportunities in emerging markets across Latin America and Asia, as well as in commercial and urban security applications. Its strategic partnerships with major defense contractors and ability to integrate with existing infrastructures further strengthen its position in the evolving counter-UAS ecosystem.


Expert commentary
Open platform video technology software is more than just a product; it's a tool that helps customers achieve their desired business outcomes. Safety, round-the-clock security, and increased operational efficiencies are now the norm due to video technology. Responsible Technology Despite humanity’s impressive technological advances, we also recognize the immense responsibility that comes with technological innovation. It's not enough to focus solely on the positive impact video technology can make, we must also be vigilant in identifying and addressing any potential negative consequences it can have on society and its citizens. This is the role of Responsible Technology. Data privacy We want to use all the good things that technology innovation brings, whether it be video, AI, ML, facial recognition, etc. We want to use all the good things that technology innovation brings, whether it be video, Artificial Intelligence, machine learning, facial recognition, etc. to serve people in societies in a responsible way. That means making sure that we regulate technology in a way that respects human rights and data privacy. Addressing the challenges The challenge is, that rather often technology leaders and policymakers either have conflicting interests or collaborate too late. To be responsible, business leaders must support their societies and policymakers in making regulations in the interest of the common good. At Milestone Systems, we are actively looking at how we develop our software responsibly, how our partners responsibly sell our software, and very importantly, how our customers use our software with a responsible mindset. Ensuring good corporate governance As a long-time partner within the security industry, we’re celebrating our 25th Anniversary this year, we are supporting the regulation of video technology for the good of society. However, it of course needs to strike the fine line between the right legislation and not hindering innovation. UNGP The UNGP is the most authoritative and widely adopted set of principles for responsible business At Milestone Systems, we want to play an active role in this and that is why we have pledged our support to the UN's Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights (UNGP). The UNGP is the most authoritative and widely adopted set of principles for responsible business. The principles call on governments and companies to identify, prevent, mitigate, and remedy actual and potential human rights abuses. Since its launch in 2011, the UNGPs have received wide support from states, civil society organizations, and the private sector, making them the key global foundation for business and human rights. Protect, respect, and remedy Through this commitment, we are taking steps to ensure good corporate governance and ethical standards in the development of our technology. We're generating mechanisms to prevent misuse and we are building educational practices internally. Based on the UNGP’s three pillars: protect, respect, and remedy, we are developing a set of Responsible Technology Principles and procedures for the development, selling, and use of our products. Need for video technology regulation In addition, we are currently evaluating all the various technology areas in which our video software can be used, such as with third-party integrations that utilize e.g., facial recognition. We are mapping out the advantages and disadvantages for societies. One key area of concern is how local authorities are mapping and storing data about us as individuals. This is the reason why we're inviting more legislation to regulate video technology rather than less. Engaging With policymakers We are meeting ministers and trade organizations as we believe this needs to be a joint effort where all parties are heard We are proactively reaching out to and connecting with policymakers and other relevant stakeholders to discuss our approach to and take on Responsible Technology and encouraging the political landscape to work with us around regulation and legislation. We are meeting ministers and trade organizations as we believe this needs to be a joint effort where all parties are heard and where we can openly weigh the advantages and the challenges of technology, whether it is video, facial recognition, machine learning, Artificial Intelligence, or other technologies. Striking a balance Implementing Responsible Technology is a journey, not a destination. To give it the focus needed, we have created a dedicated team to implement this initiative at Milestone Systems. At the same time, we are reaching out to the political landscape to discuss how we balance regulation without hindering innovation. Video technology used ethically We are a global company with worldwide operations, and we are having dialogues about how video technology is being used and how we can have meaningful talks about what regulation and legislation should look like. However, we don’t necessarily want to limit access to the technology itself. Facial recognition We encourage the policymakers to engage with us in the industry so that together we can strike the fine line Facial recognition is a great example of this. The EU is considering making live facial recognition illegal. That would be a huge inhibitor of proactive terrorism prevention. For example, if a well-known terrorist is walking down the street and is being mapped out against Interpol’s most wanted list, the authorities should be able to react. However, if a person walking down the street but is not mapped out or does not have any priors then the city should not be allowed to store the data of that individual’s whereabouts at that point in time. This potential legislation is concerning to me as a citizen of Europe. Instead, we encourage the policymakers to engage with us in the industry so that together we can strike the fine line for the better good of all of us. Maintaining high ethical standards We have a firm understanding and expectation that ethical standards are a huge driver in the security business. Citizens are not in favor of technology companies abusing data about them and monetizing from things that they have not opted in to do. Soon, I think we will see many more companies and governments leaning toward suppliers that do have a responsible mindset and high ethical standards for partnerships. Ethical practices Our journey toward Responsible Technology is an ongoing process, and we must remain steadfast in our commitment to ethical practices and the protection of human rights. We recognize that the rapidly changing technological landscape continually presents new challenges and opportunities. For this reason, we continuously look into how we can improve, for example, our end-user license agreements to avoid potential human rights abuses. An industry responsibility Security companies must prioritize careful planning and preparation, including developing policies and procedures For Responsible Technology to truly become a reality, compliance with international human rights laws and data privacy regulations is critical. Security companies must prioritize careful planning and preparation, including developing policies and procedures that govern the ethical use of video surveillance systems. The secure and ethical community In today's technology environment where deep integrations, machine learning, and artificial intelligence are becoming the norm, Responsible Technology is more relevant than ever. The security industry has a unique opportunity to set an example for other sectors by promoting a secure and ethical development community that prioritizes Responsible Technology, trustworthy data collection, and the protection of human rights. We must all rise to this challenge and embrace our role as ethical leaders for the greater good of both people and societies.
Inadequate security measures on your essential infrastructure can have severe consequences. Consequences Consider the rail industry: If a vandal cuts the cables on a vital mechanism that controls train signals, train safety is jeopardized. To avoid train collisions or derailments and thus significant damage to property and potential loss of life, the operating company must shut down the service until the infrastructure is repaired and the network is up and running again. The disruption affects the rail ecosystem itself, but also the people using the trains, the transportation of cargo, and more. The financial cost of repairing the damage, restoring signal functionality, and compensating for delays can be substantial. For another example, consider electrical substations: A fire or targeted attack can damage the system and lead to devastating power outages. Traditional surveillance limitations Traditional video surveillance has its limits when it comes to protecting transformer stations Traditional video surveillance has its limits when it comes to protecting transformer stations. The facilities are often located in rural areas, where straying animals or flying leaves trigger false alarms. 3D Surveillance solutions overcome these challenges by volumetrically securing the area and immediately detecting intruders only raising the alarm in the event of a human intruder and even identifying drone attacks. Protecting critical infrastructure with 3D surveillance Critical infrastructure must be monitored. It remains at risk if operators do not have systems for monitoring entire areas rather than just the periphery if security personnel has limited information in case of an intrusion and if security response protocols are not automated. 3D Surveillance solutions 3D Surveillance is an important tool for protecting critical infrastructure and ensuring the safety of those who rely on it. Integrating LiDAR technology, 3D Surveillance solutions provide a comprehensive view of the area being monitored with real-time monitoring and response, protecting critical infrastructure from damage and providing a more comprehensive security system. Advanced analytics and artificial intelligence Security personnel can identify and verify threats more easily and track the movements of individuals or vehicles, as well as respond to incidents as they happen. 3D Surveillance systems can be equipped with advanced analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities to detect patterns and anomalies that may indicate a potential threat. This can help to prevent potential attacks or accidents before they occur, as well as enable more accurate responses to incidents. Talent challenge Turning to autonomy by implementing sensor- and software-based solutions requires fewer if any, in-person patrols 3D Surveillance can also help tackle the talent challenge in the industry: Recruiting security professionals involves extensive background checks, and jobs in the industry are notorious for their low salaries, which results in high staff turnover. Turning to autonomy by implementing sensor- and software-based solutions requires fewer if any, in-person patrols and ensure reliable infrastructure protection. Additional security measures In many countries, more stringent legislation now mandates the implementation of additional security measures to safeguard critical infrastructure, particularly at a country's points of entry, such as airports and harbors. Protecting the perimeter is no longer enough. For instance, airport management must ensure that critical areas, including the space around aircraft and near unauthorized access points, are secure. While multi-layered screening of individuals at the perimeter is a valuable security measure, it must be complemented by smooth and efficient surveillance of the entire area, which can only be achieved through advanced technology. Different adoption rates 3D Surveillance technology is only beginning to gain traction in most locations, and adoption rates differ significantly from one region to another. For instance, Scandinavia and Eastern Europe have embraced 3D Surveillance to a greater extent than Western Europe. Regions with lower adoption rates will likely catch up as they seek to reinforce the security of their critical infrastructure, especially given the conflict in Eastern Europe. Vandalism and damage protection 3D Surveillance enhances the security of critical infrastructure, reduces the risk of downtime and loss of revenue 3D Surveillance offers reliable protection against vandalism and damage - major concerns for companies that rely on critical infrastructure. LiDAR-based, software-enhanced 3D Surveillance solutions provide real-time insights and enable automatic processing of the information so that operators can autonomously and quickly detect and respond to potential threats. These solutions are scalable and customizable, allowing companies to adapt their security measures to their unique needs and changing environments. 3D Surveillance enhances the security of critical infrastructure, reduces the risk of downtime and loss of revenue, and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements. Asset management and maintenance planning Beyond its security benefits, 3D Surveillance can help with tasks such as asset management and maintenance planning. It can help identify potential problems or maintenance needs before they become more serious issues by providing a real-time view of the monitored infrastructure. This can help to reduce downtime and keep critical infrastructure running smoothly. Real-time management The same technology can also perform volume monitoring tasks and thus facilitate the management of valuable resources such as bulk material, grain, wood chips, or chemicals. By scanning the stock 24/7 and automatically calculating stock volume updating records in real-time, this technology supports lean production systems and automated processing.
The security industry is going increasingly digital these days, with more small- and medium-sized businesses joining their global brethren by moving their data to the cloud, leveraging the benefits of artificial intelligence, and embracing more open solutions. Innovation is expected to continue at a rapid pace, thanks in part to the residual effects of the pandemic which has driven changes that might have otherwise taken five years or a decade or more to get into customers’ hands on a global scale. Let’s take a look at the trends that will dominate ISC West 2023. Improved analytics Analytics is about expedience, and in the surveillance world, it makes it possible to identify and search for the “who did it?” clip you need. For analytics, along with the cloud, it comes back to the core themes of being able to do more with technology Analytics also provides more actionable intelligence than a simple surveillance camera may provide, from identifying high-traffic areas during select times of the day and alerting staff to pay greater attention to these areas, to business intelligence that can enable a company to staff a store with more employees. For analytics, along with the cloud, it comes back to the core themes of being able to do more with technology and relying less on humans. Leveraging the cloud The cloud story is very related: it provides the ability to perform video-related tasks from anywhere on any device. In addition, the cloud makes it easier to share videos with other stakeholders and collaborate on investigations. By storing video on the cloud, end users reduce their total cost of ownership because they no longer have to invest in onsite storage solutions, while gaining greater storage capabilities and thereby future-proofing their solutions. Deployment patterns Because the cloud requires a less total cost of ownership and can be intuitive, it is driving interest in solutions Another interesting trend that we’ll be hearing more about this year is the overall deployment patterns of video surveillance systems. This is part of the cloud trend, but the broader trend is the amount of effort it takes to deploy, monitor and maintain the video surveillance system. Because the cloud requires less total cost of ownership and cloud access can be intuitive, it is driving interest for solutions that can be hosted in the cloud. Interoperability vs. proprietary Related to the debate of open vs. closed solutions is how much the surveillance market prefers a turnkey solution compared to a more custom best-of-breed and tailored solution. Smaller and mid-market companies will be more interested in the turnkey solutions provided by a single vendor, while enterprise-level companies traditionally gravitate toward investing in customized solutions that are more likely to address their unique security challenges. One other related trend to keep an eye on is the role of the integrator as part of the rise of cloud and Video Surveillance as a Service (VSaaS) offerings.
Security beat
Technology is driving new opportunities in the security industry. Innovation trends include artificial intelligence (AI), edge-based systems, mobile systems, a greater focus on software, and efforts to simplify operation of security systems, even as capabilities become more complex. ISC West 2022 reflected these changing trends. “In addition to emphasizing technology innovation, ISC West also reflected an industry that is resilient, dedicated and passionate,” said Mary Beth Shaughnessy, the Event Director of ISC Security Events. ISC West 2022 “Almost 12,000 dealers, installers, integrators, end users and consultants reconnected at ISC West 2022, and there were nearly 20,000 total industry professionals in attendance (including manufacturers),” adds Mary Beth Shaughnessy. The 550 exhibitors and brands on display reflected an industry that has come through the COVID-19 pandemic in better shape than ever, poised for even greater success in the years ahead. Turning video and access control into knowledge Deployment of AI to ‘watch video’ can inform users of what’s happening in real-time Motorola Solutions emphasized several themes that were heard repeatedly throughout the show. “One trend is fulfilling the need to turn video and access control into sources of knowledge, inside the enterprise,” said John Kedzierzski, Motorola Solutions’ Senior Vice President of Video Security and Access Control. Deployment of AI to ‘watch video’ can inform users of what’s happening in real-time, while monitoring access control yields the equivalent of an operating system inside a building. Using the Cloud offers consumer ease-of-use to systems The second trend listed by Motorola Solutions is working to bring the consumer ease-of-use experience into enterprise security solution applications. Professional security systems were previously complicated to buy, install, manage and upgrade. However, using the Cloud, even distributed enterprises can bring consumer ease-of-use to systems, from improving the out-of-box installation experience to boosting the ability to manage the system. Transition to ‘mobile first’ interfaces The third trend emphasized by Motorola Solutions is transition to ‘mobile first’ interfaces, reflecting the need for busy security executives to be on-the-go, but with full access to their systems, without being chained to their desks. Since the last springtime ISC West show in 2019, Motorola Solutions has grown rapidly, both organically and through acquisition of IndigoVision, Pelco, Openpath, Envysion, and Ava Security. Cloud-based Orchestrate system Integration is simple through a ‘drag-and-drop’ approach that doesn’t involve writing code In addition, the company is making it easier to integrate video and access control systems with Motorola’s radio systems, typically carried by security guards. The cloud-based Orchestrate system translates ‘events’ from access control and video, to trigger notifications on a mobile radio. Integration is simple through a ‘drag-and-drop’ approach that doesn’t involve writing code. Simplifying implementation of AI Artificial Intelligence (AI) has traditionally been associated with the use of large servers or even intelligence in the Cloud. Several exhibitors at ISC West helped to change that misconception. For example, Oosto offers a simpler and more economical approach. They supply edge appliances for AI. The purpose-built Vision AI appliance, a small box, puts intelligence at the ‘near edge’, by connecting to up to five cameras. Easy and dependable ‘failover’ ensures redundancy without a big investment, and the system can work with any IP camera, including an end user’s installed base of cameras. Oosto’s TCO (total cost of ownership) calculator Oosto’s TCO (total cost of ownership) calculator spells out how much a customer can save versus using a big server, including lower costs such and power and cooling. AI was probably the biggest buzzword at ISC West, but there was also emphasis on the practical results of applying AI to physical security. Artificial Intelligence (AI) - the biggest buzzword at ISC West I believe our purpose is to bring buzzwords, like Cloud and AI together in a way that is useful to end-users" “What surprises me (at the show) is that there is a lot of generic marketing of AI, but we are trying to step back from our analytics and look at applications that serve certain end-users,” said Jeff Corrall, Vice President - Product Management at March Networks, adding “As an industry, we are still at the stage of AI as a buzzword.” Jeff Corrall further said, “I believe our purpose is to bring buzzwords, like Cloud and AI together in a way that is useful to end-users. We have to live with the buzzwords, but what we really want is to apply them. That creates a stickiness with the end-user — when high technology is making a difference.” March Networks Labs address specific end-user problems and then apply their systems to provide a solution. Jeff Corrall adds, “A lot of AI is responding to what the customer is asking for, and we are stepping back and making sure the end-user will use it on a consistent basis.” ‘Edge versus cloud’ was a common theme at ISC West Edge versus Cloud ‘Edge versus cloud’ was a common theme at ISC West, pondering where in a system the ‘intelligence’, such as AI and machine learning, as well as other functionality, should reside. Among the companies addressing the quandary was Axis Communications, which focused on the issue using a racing theme at their presentation to the industry press. The winner of the ‘race?’ - The combination of both approaches working together as a team, of course. AXIS Speed Monitor on exhibit One introduction at the show was the AXIS Speed Monitor, a speed detection app available using ACAP Axis Communications also highlighted the deep learning analytics of the ARPEC 8 camera chip (introduced during the COVID-19 pandemic), which will be deployed across their camera line. One introduction at the show was the AXIS Speed Monitor, a speed detection app available using ACAP (Axis Camera Application Platform), the capability to load ‘apps’ onto camera chips at the edge. They also introduced the D4100-E Network strobe siren (a smart edge device), the Audio Manager Pro (a cloud-based software system enabling zoning and callouts for specific areas in a building), the W101 body worn cameras with GPS capabilities, and a Barcode Reader for doorstop applications (another ACAP app). ‘App Store’ approach to expanding applications Azena is at the center of expanding applications at the edge, promoting new applications through an ‘App Store’ approach that sells software apps that can be loaded onto cameras that are equipped with Azena’s operating system. In the last couple of years, the company (formerly known as Security and Safety Things) has expanded its offerings. There are currently 108 apps in the store from 30 to 40 app developers. There are 14 camera models (from six manufacturers) that are commercially available and run their operating system. The newest camera is a fisheye model from Vivotek. “What we have seen is that a lot of the use cases are pretty unique,” said Fabio Marti, Vice President - Marketing for Azena. Two examples are an application that monitors a flame to ensure it is burning cleanly (no smoke). Another system monitors nets covering fish farms to avoid birds getting tangled up in the nets. Fabio Marti said “A challenge is to find new business avenues for integrators. Everybody is not eager to look beyond their comfort zone.” Focusing on software to ensure user experience Software systems are one of the major focal points for innovation in security systems Software systems are one of the major focal points for innovation in security systems and Verkada is focusing on how software innovation can improve systems. “For decades, innovation was on the hardware front,” said Filip Kaliszan, Verkada’s Founder and Chief Executive Officer (CEO), adding “We saw an opportunity for more innovation on the software side. The customer experience revolves around software.” Ensuring an end-to-end experience “We want to guarantee an end-to-end experience,” adds Filip Kaliszan. As a new company with a ‘hybrid cloud’ approach, Verkada focused on appealing to end users to convince them of the value proposition. Once an end user was convinced, Verkada brought in an integrator partner to deliver the solution. In effect, Verkada finds demand and brings that demand to the integrator. Software-centric operation of a modern building Verkada is broadly focused on ‘software-centric operation of a modern building.’ After starting out in video, Verkada has since expanded into systems for access control, alarm systems, and other categories. They use a combination of third-party hardware and equipment that is custom designed to work seamlessly with their software systems. Verkada’s end goal is to put the various systems together into a platform. They will continue building each product category, which will eventually be unified into ‘the operating system for the building of the future.’
The UK Government has been working to reduce the risks associated with illegal drone use since a high-profile incident at UK’s Gatwick Airport in December 2018, when a drone sighting triggered a three-day shutdown of the UK’s second busiest airport, disrupting the travel plans of 140,000 people and affecting 1,000 flights. To address growing security threats by drones, the UK Government has released its ‘Counter-Unmanned Aircraft Strategy’. ‘Counter-Unmanned Aircraft Strategy’ This strategy sets out our approach to countering the threat the malicious or negligent use of drones can bring" “This strategy sets out our approach to countering the threat the malicious or negligent use of drones can bring,” says Brandon Lewis, the U.K. Minister of State for Security. “It will provide the security the public and drone users require to continue to enjoy the benefits of leisure and commercial drone use and facilitate the growth of the drone industry.” “Given the challenge posed by rapid advances in drone technology and the potential threat, the strategy will provide overarching direction to our efforts,” says Lewis. The strategy focuses on ‘small drones’, those weighing less than 20 kg (44 pounds). Countering malicious use of aerial drones The UK Counter-Unmanned Aircraft Strategy centers on mitigating the highest-harm domestic risks resulting from malicious use of aerial drones. They are: Facilitating terrorist attacks, such as modifying commercially-available drones to conduct reconnaissance or attacks. Facilitating crime, especially in prisons, where drones are currently used to deliver contraband. Disrupting critical national infrastructure, such as airports, where a malicious incursion using a drone can have serious safety, security and economic consequences. Potential use by hostile state actors. Maximizing benefits of drone technology The initiative will also look to build strong relationships with industry to ensure high security standards Over the next three years, the strategy will seek to reduce the risks posed by the highest-harm use of drones while maximizing the benefits of drone technology. It will develop a comprehensive understanding of evolving risks and take a “full spectrum” approach to deter, detect and disrupt the misuse of drones. The initiative will also look to build strong relationships with industry to ensure high security standards. Further, promoting access to counter-drone capabilities and effective legislation, training and guidance will empower the police and other operational responders. Tactical response to drone-based threats Because technology is rapidly evolving, the response needs to keep pace, according to the strategy document. Lewis adds, “We will therefore work to understand how drone-based threats might evolve in the future, both at the tactical and strategic levels.” The strategy will be to build an end-to-end approach to tackling the highest-harm criminal use of drones. It will also work to make it easier to identify malicious drone use against a backdrop of increased legitimate use. Legal drone operators will be required to register with the Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) and to pass an online competency test before flying a drone. Retailers who follow a specific set of safety guidelines when selling drones will be designated ‘DroneSafe’. Unmanned traffic management system The government is working toward future implementation of an unmanned traffic management (UTM) system, which provides a means of preventing collisions between unmanned aircraft and other manned or unmanned aircraft. The current strategy includes early planning for the system. An Industry Action Group will ensure a continuing relationship with the drone industry and help to improve existing counter-drone measures and identify new opportunities, such as use of ‘Geo-Fencing’ to restrict drones from flying in certain areas. Regulating commercial and domestic drones The UK Department of Transport is responsible for safe and lawful use of drones within the UK airspace The strategy will seek to communicate the UK’s security requirements to the counter-drone industry and to encourage a thriving sector that is aware of, and responsive to, the needs of government. Regulating drones is the responsibility of two UK government departments. The UK Department of Transport is responsible for safe and lawful use of drones within the UK airspace, while the Home Office has overall responsibility for domestic counter-drone activity. Fast-evolving drone and counter-drone technology Also, the Center for the Protection of National Infrastructure (CPNI) has been involved in reducing the vulnerability of sensitive sites, including airports. New performance measures will track the strategy’s success. Due to the fast-evolving nature of drone and counter-drone technology, the intent is to review and, if necessary, refresh the strategy in three years.
A week of mass shootings this summer has again spotlighted the horror of gun violence in public spaces. A 19-year-old gunman opened fire at the Gilroy Garlic Festival in California on July 28, injuring 13 and killing four (including the gunman). In El Paso, Texas, less than a week later, a lone gunman killed 22 people and injured 24 others. In Dayton, Ohio, a day later, a gunman shot 26 people during a 30-second attack, killing 9 and injuring 17. Rising active shooting incidents Beyond the grim statistics are three distinct incidents, linked only by the compressed timeline of their occurrence. Still, there is a tendency to want to find a pattern: Why do these incidents happen? How can we prevent them? In total, 91 people were killed and 107 more were injured in locations such as workplaces, schools, and public areas One attempt to analyze trends and commonalities among mass shooting incidents is a research report published by the U.S. Secret Service National Threat Assessment Center (NTAC) titled “Mass Attacks in Public Spaces – 2018.” Looking at the totality of major mass attacks last year, the report seeks to find patterns that can shed light on the attacks and suggest strategies to prevent and mitigate future incidents. Mass shootouts Between January and December 2018, 27 incidents of mass attacks – in which three or more persons were harmed – were carried out in public spaces within the United States. In total, 91 people were killed and 107 more were injured in locations such as workplaces, schools, and other public areas. The National Threat Assessment Center report considered all the mass attack incidents in 2018 and analyzed some trends and statistics: Over half (59%) took place between the hours of 7 a.m. and 3 p.m., and 63% of the attacks ended within 5 minutes of when they were initiated. Most of the attackers were male (93%); the youngest was a 15-year-old student and the oldest was 64. Nearly a fourth of the attackers (22%) had substance abuse problems, and half (48%) had a criminal history, whether violent or non-violent. About two-thirds (67%) experienced mental health symptoms, commonly depressant and psychotic symptoms such as paranoia, hallucinations or delusions. Almost half (44%) had been diagnosed with a mental illness prior to the attack. The main motives were domestic, personal or workplace grievances (52%); followed by mental health/psychosis (19%); 22% had unknown motives. Most (85%) of attackers had at least one significant stressor in their lives in the last five years; 75% had experienced stressors that occurred in the previous year before the attack. Personal stressors included the death of a loved one, a broken engagement of physical abuse. Work- or school-related stressors included losing a job, being denied a promotion, or being forced to withdraw from classes. More than half of attackers (56%) experienced stressors related to financial instability. Personal issues such as homelessness or losing a competition were also stressors. Nearly all the attackers (93%) engaged in prior threatening or concerning communications. Most of the attackers (78%) also exhibited behaviors that caused concerned in others. For the majority of the attackers (70%), that concern was so severe that others feared specifically for the safety of the individual, themselves, or others. The Secret Service report also analyzed the overall impact of several factors: Mental health and mental wellness - Mental illness, alone, is not a risk factor for violence, and most violence is committed by individuals who are not mentally ill. Two-thirds of the attackers in this study, however, had previously displayed symptoms indicative of mental health issues, including depression, paranoia, and delusions. Other attackers displayed behaviors that do not indicate the presence of a mental illness but do show that the person was experiencing some sort of distress or an emotional struggle. The importance of reporting - Since three-quarters of the attackers had concerned the people around them, with most of them specifically eliciting concerns for safety, the public should be encouraged to share concerns they may have regarding coworkers, classmates, family members, or neighbors. Need for a multidisciplinary threat assessment approach - There is a need to standardize the process for identifying, assessing, and managing individuals who may pose a risk of violence. Law enforcement and others are taking steps to ensure that those individuals who have elicited concern do not “fall through the cracks.” Law enforcement personnel should continue developing close partnerships with the mental health community, local schools and school districts, houses of worship, social services, and other private and public community organizations. Threat assessment Threat assessment refers to a proactive approach to violence prevention, an investigative model Many of the resources to support the threat assessment process are already in place at the community level, but require leadership, collaboration, and information sharing to facilitate their effectiveness at preventing violence, according to the report. ‘Threat assessment' refers to a proactive approach to violence prevention, an investigative model originally developed by the U.S. Secret Service to prevent assassinations. It has since been adapted to prevent all forms of targeted violence, regardless of motivation, including K-12 school shootings and acts of workplace violence. When implemented effectively, a threat assessment generally involves three key components: Identify, Assess and Manage. Identify, Assess and Manage Public safety entities rely on people who observe concerns to identify the individual to law enforcement or to someone else with a public safety responsibility. In educational settings or workplaces, concerns may be reported to a multidisciplinary threat assessment team that works in conjunction with law enforcement when needed. The responsible public safety entity is then tasked to assess the situation to determine how they can manage any risk of violence posed by the individual.
Case studies
One of Australia’s pioneering fully integrated property groups, Charter Hall has more than 31 years of experience in funds management and property investment in the core sectors of office, retail, industrial and logistics, and social infrastructure. Having carefully curated a diverse AUD 61.3 billion portfolio of more than 1,500 high-quality long-leased properties, partnership, and financial discipline are necessarily at the heart of Charter Hall’s approach to commercial real estate. Acting in the best interest of its customers and communities, the company combines insight and inventiveness to unlock hidden value and nurture a development pipeline of more than AUD 9 billion that, long term, will deliver sustainable, technologically enabled projects for Charter Hall customers. Challenge Charter Hall is committed to exploring ways to leverage technologies to ensure security for buildings Charter Hall is committed to continuously exploring ways to leverage the latest technologies to advance sustainability and ensure security for its buildings and their surroundings. To that end, the company developed the Charli workplace app to provide its building communities with a range of services, features and benefits to create valued experiences that are convenient for its tenants. From concierge services to building updates and alerts, Charli was designed to keep tenants connected with the broader workplace community and provide tenant managers with quick, convenient access to Charter Hall’s property management services for service requests and to report or log issues. Mobile access control Charter Hall recognized that integrating mobile access control into the app would optimize the role Charli could play in achieving a frictionless yet secure and sustainable tenant experience. “At the same time, we wanted to streamline our access technology by deploying universal readers across Charter Hall properties in tandem with mobile IDs, so access could be easily adapted for each building but still controlled at a central point,” said Loren Mellowship, General Manager - Wesley Place, who oversees the company’s three adjacent Wesley Precinct buildings in Melbourne. Solution Charter's Operations Team opted to deploy HID Mobile Access and Signo Readers for access control Building upon its existing relationship with HID, Charter Hall’s National Operations Team opted to deploy HID Mobile Access and HID Signo Readers for access control. Ensuring that everything was integrated for both Charter Hall and its tenants was a crucial part of the solution. The access control system became a foundational layer to build upon by pulling together all the disparate systems in the buildings. This was done not only through the readers, but also by utilizing an API-based approach wherever possible. HID Mobile Access HID Mobile Access lets any compatible mobile device be used as a credential to securely access doors, gates, networks, and more. It significantly increases convenience and boosts operational efficiency without compromising security. By eliminating the need for physical access cards to move throughout buildings and to access secure areas including parking, printers and lockers, the mobile access solution also reduces costs. Critical to the success of any technology investment and deployment is the involvement of key stakeholders throughout the process, as well as futureproofing and ensuring the longevity of the solution. This is true whether that investment affects a single asset or is portfolio-wide. HID Signo Reader HID Signo Reader supports the widest range of credential technologies via native Bluetooth and NFC To that end, the highly versatile HID Signo Reader supports the widest range of credential technologies via native Bluetooth, Near Field Communication (NFC), and Apple Wallet. It delivers unparalleled performance with ultra-secure storage of cryptographic keys and a connection to the future through secure bidirectional communication support. Each reader is also designed to be connected and managed remotely for easy upgrades. “We took a precinct approach, which is why HID was ultimately selected. Everything is now on the same backbone, which makes it a lot easier to manage what is going on, and everything is talking to the same central point,” said Mellowship. Result In conjunction with Charli, Charter Hall tenants, and employees can now use their handsets to access the entire Wesley Precinct and its amenities, including end-of-trip facilities and FollowMe Printing. Charter Hall tenants and employees can now use their handsets to access the entire Wesley Precinct Self-onboarding for the building also allows the tenant to request and receive access any time of the day—without the delays of waiting for a physical card, phone call, or someone to come to the building. “No one forgets their mobile device so they can use their mobile ID as a backup if they forget their physical card. Security guards also save time when new credentials need to be issued. It may only take 30 seconds to open a second app to do that, but if you’re doing 1,000 cards over a year that multiplies quickly. So, integration makes things more efficient. It saves time,” said Mellowship. Charli app About 4,000 people in Charter Hall’s Wesley Precinct will be leveraging HID Mobile Access via the Charli app. Though no benchmark metrics are available for comparison yet, the company and its tenants are realizing significant savings through greater productivity thanks to managing access building-wide through a single app and streamlined remote credentialing. Savings are also realized through the elimination of costs associated with issuing physical access cards as well as deactivating and replacing them when they are lost or stolen. “HID Mobile Access allows secure, seamless access from street-to-seat and frees up everyone to focus on more valuable work,” said Mellowship.
Databuoy Corporation, a gunshot localization and real-time emergency alert intelligence system, and the Philadelphia Police Department announced that SHOTPOINT, Databuoy’s life-saving gunshot localization and detection system, has been selected by the Department for a pilot program to help to reduce gun violence throughout the city. With gun violence on the rise, officials sought a solution that could accurately detect a gunshot and localize where it came from, to prosecute more offenders and hopefully lessen the number of incidents. When public safety is at risk, having real-time systems that seamlessly communicate vital information is key for first responders. Databuoy's SHOTPOINT system Databuoy's SHOTPOINT system can be deployed in nearly any environment with near-perfect results. SHOTPOINT eliminates false positives, without human intervention, and provides accurate, quickly deployed reports to first responders. “Our system works reliably in high noise environments and around vehicular traffic without false detections,” Kathleen Griggs, Databuoy CEO said. “The system is automated and gets information to responding officers instantly and has supported police response and investigations for multiple homicides in the years we have been installed.” Game-changing technology SHOTPOINT is becoming more accessible to cities since it has been awarded MAS contract by GSA SHOTPOINT is a game-changing technology that is unsurpassed in its detection and location accuracy and one that law enforcement and security clients can trust. “We are deployed in some of the most volatile environments in the country, like the Fremont Street Experience in Las Vegas,” says former CBP Commissioner, David Aguilar, one of Databuoy Corporation’s Board of Advisor Members. “We are confident it will do the same for the City of Philadelphia.” SHOTPOINT is becoming more accessible to cities since it has been awarded a Multiple Award Schedule (MAS) contract by the General Services Administration (GSA) on a Service-Disabled Veteran-Owned Small Business (SDVOSB) contracting vehicle and is available on The Interlocal Purchasing System (TIPS) through a Minority Owned 8(a) Small Business. Pilot program “We are committed to the safety of our citizens,” Robert Keehfuss, Philadelphia Police Department, Public Safety Technology Program Manager said. “Philadelphia needs a system that will instantly give us the precise location where the shot occurred. Every second counts when it comes to saving lives and catching shooters, so the faster we get the detailed information, the better chance we have of protecting our citizens.” The pilot program between Databuoy and the Philadelphia Police Department will be ongoing for the next several months and cover one of the city’s heaviest gun violence areas. If the system performs to the goals outlined in the pilot, there is support for a larger rollout plan.
Cozaint Corp, the developers of intelligent surveillance solutions, has been selected by the Pascua Yaqui Tribe Police Department in Tucson, AZ, to deliver the BOBBY physical security tower to provide a “safe zone” location for local citizens to conduct sales transactions, custody transfers, or other dealing where a security monitored area would provide a safe setting. Cozaint’s BOBBY platform of physical security kiosk tower provides 24/7 situational awareness for organizations of all sizes with various IoT security sensors, constant video surveillance, and tied to a remote monitoring center. Cozaint BOBBY kiosk tower The Cozaint BOBBY kiosk tower also has a 27” interactive display that displays information about local tribal activities as well as allowing for visitors to activate a “panic button” if they feel threatened. The BOBBY “safe zone” tower is connected to the tribal police department where officers can see and speak with the user to determine if an emergency exists and how best to respond. “With certain transactions occurring between complete strangers —such as online sales— sometimes our community may wish to meet at a more secure location where video surveillance and the ability to reach one of our officers in an emergency is all in one safe zone,” said LT. Elizabeth Esparza of the Pascua Yaqui Police Department. BOBBY safe zone tower BOBBY safe zone tower delivers peace of mind to Pascua Yaqui Police Department and its citizens With 360-degree video surveillance coverage and 24/7 video recording, the BOBBY safe zone tower delivers the peace of mind that the Pascua Yaqui Police Department and its citizens are looking for to safely meet others with eBay or other sales transactions, when custody transfer events occur, or other interactions where a safe and monitored location is preferred. “Our BOBBY tower unit is an ideal community safe zone security platform, where users can rest assured that they are being monitored for safety and security reasons when dealing with various transactions with others in the community,” stated Jay Jason Bartlett, CEO, Cozaint, adding “Interacting with the Pascua Yaqui Police team in the event of an emergency provides an additional level of security for the local community.” BOBBY tower unit The BOBBY tower unit also displays local community information as well as current events, helping to keep the community up to date on what is happening throughout the tribe. This particular BOBBY tower unit is located on tribal land in the desert of Tucson, AZ, where the summer rains and high temperatures create harsh operational conditions for an outside device such as this.
Asio Technologies, a pioneering developer and manufacturer of tactical solutions for defense, security, and paramilitary applications, has fulfilled a follow-on order from the IDF and recently delivered thousands of additional Orion Systems. Asio Technologies solutions, including the Orion systems, are already in operational use by the IDF. Orion (or OLAR/AMUD–as called by the IDF) is a rugged and secured mobile system for dismounted forces, enabling mission planning and real-time navigation. Using the Android platform, Orion enables mission planning, positioning, and enhanced situational awareness using the GIS database and augmented reality (AR) capabilities. Orion system Orion System can communicate and interface with other Asio Technologies tactical solutions With both online and offline operation modes, Orion serves the individual soldier or commander up to the battalion level, allowing them to get real-time updates from each other regarding friendly and hostile forces, as well as other mission-critical information. It is a scalable, multilayered, networked situational awareness solution with a highly intuitive and interactive palm-size interface. The Orion System can communicate and interface with other Asio Technologies tactical solutions, such as the LYNX tactical handheld day/night augmented reality situation awareness system and RIGEL tactical smartwatch, to provide a fully integrated tactical combat suit for ground forces. Delivery of Orion Systems to the IDF completed David Harel, Asio Technologies CEO, said, "Another delivery of Orion Systems to the IDF was completed, with additional thousands of units provided to the IDF's ground forces. We are honored to be chosen by the IDF once again, and see this as a sign-of-proof of the added value our solutions provide." He adds, "Bringing all the needed information to the palm of their hands, our Orion Systems allow the maneuvering force to plan and complete their missions quickly and effectively."
Finland’s Osuuskauppa PeeÄssä retail co-operative, a nationwide S-Group co-operative federation member, has deployed March Networks video surveillance systems across its footprint of 73 retail and service establishments. The co-op boasts 121,000 customer owners in Finland’s Northern Savonia region, whose capital and largest city, Kuopio, is 384 kilometers north of Helsinki. The 73 retail and service locations include three Prisma Hypermarkets, 29 S-Market grocery stores, 15 convenience stores, 15 restaurants, six ABC gas stations, three hotels, a SOKOS department store, and a Kodin Terra hardware store. March Networks video surveillance systems The rollout began in September 2019 and currently includes 85 March Networks recorders, a mix of 8000 Series Hybrid NVRs and 9000 Series IP Recorders, and more than 1,500 March Networks cameras. A new hotel and supermarket currently under construction will bring the camera count close to 2,000. “We used to have several different video surveillance systems and 10 different camera models from six manufacturers,” said Kimmo Keränen, IT Manager for PeeÄssä retail co-operative. “Maintenance was almost impossible and the picture quality in some cases was very poor.” Time management challenge Central management was a key feature for PeeÄssä retail while looking for in its new surveillance system “On top of that, there was no synchronized timekeeping, so one system could be five minutes off and another one could be an hour off. That was a real problem because correct timekeeping is everything when you’re looking for evidence.” For this reason, central management was a key feature PeeÄssä retail co-operative was looking for in its new surveillance system. “A majority of the 19 S-Group regional co-ops were already using March Networks systems, so the decision was easy to make,” said Jan Österlund, ICT Manager with SafeIT, a systems integrator and March Networks Certified Solution Provider serving the S-Group and PeeÄssä accounts. Central monitoring and management With more than 1,000 NVRs and tens of thousands of cameras across the larger S-Group co-ops, central management is a huge timesaver. Österlund can push out firmware upgrades and device settings with a few simple mouse clicks using March Networks Command Enterprise Software. The advanced system management software is ideal for managing large distributed video surveillance architecture. Its health monitoring and mass management capabilities make it easy to look after thousands of recorders and cameras from one central location. “We can schedule upgrades by location type and opening hours to minimize any interference with recording during business hours,” explained Osterlund. Recorders and cameras in use The 8000 and 9000 Series recorders are 32-channel or 64-channel devices with either 20 TB or 40 TB of onboard storage, sufficient to capture 30 days of archived video. The majority of the 1,500 cameras are March Networks SE2 Indoor and Outdoor IR Domes, but SE2 IR MicroBullets, SE2 Pendant PTZ Domes, and legacy analog cameras are also used for specific applications. Searchlight software integration Searchlight helps organizations gather business intelligence, which can help retailers with customer service S-Group is transitioning to a new point-of-sale system and has plans to integrate it with March Networks’ Searchlight for Retail software, which will allow the co-ops, including PeeÄssä, to identify suspicious transactions and instantly link to the associated video. Searchlight also helps organizations gather business intelligence, which can help retailers with operations, marketing, and customer service. “We are looking forward to acquiring the Brickstream 3D Gen2 sensors for queue management and people counting, and March Networks ME6 IR Domes for AI-powered analytics,” said Keränen. GDPR Compliance The March Networks system in place at PeeÄssä complies with the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which came into effect in 2018 and aims to protect the personal data and privacy of EU citizens. System features like privacy masks, which allow users to block out specific parts of a camera’s field of view, are important for meeting the regulation. “GDPR compliance is one of the reasons why we recommended March Networks,” said Österlund. Video access, training, and monitoring Video is currently monitored by guards in three control rooms, but managers also have access to live and recorded video from their locations. Altogether, approximately 100 PeeÄssä staff have access to the video. “Training everyone to use the system was very easy,” remarked Österlund. “The March Networks system is very user-friendly, so we supplied step-by-step instructions on how to log in, pick a camera, play the video, and export it.” Crime management Video is regularly used to supply evidence for shoplifting and internal fraud investigations Video is regularly used to supply evidence for shoplifting and internal fraud investigations, but the much-improved video quality from the March Networks system was also welcomed by local law enforcement. The Eastern Finland Police Department has mapped the location of PeeÄssä’s publicly facing cameras in the National Police Board’s database of surveillance cameras to help access video for criminal investigation purposes. “Almost every week, we are asked for video from the police department,” said Keränen. Installation, time, and cost savings SafeIT’s experience with the March Networks deployments at other S-Group co-ops helped to streamline the installation at PeeÄssä. “We supplied local integrators with clear guidance on how to set up the cameras and NVRs,” said Österlund. Standardizing on March Networks allows the PeeÄssä co-op to save time and reduce costs for system maintenance. The state-of-the-art video surveillance system is also much easier to use. “We are very satisfied with March Networks,” said Keränen. “It was a big project, but well worth doing.”
Being isolated on the edge of wilderness means there’s a need for a video system that’s both reliable and flexible. For that reason, the team at Jackson Hole Airport (JAC) since 2009 has relied on video management software (VMS) from Milestone Systems to enhance security, safety, and efficiency. Challenge - Help to keep scaling At the edge of the frontier, Jackson Hole Airport has experienced considerable growth over the years. Significant capital investments in expansions have made new video system integrations possible several times, and Milestone XProtect has supported the airport’s needs along the way. As of 2020, over 220 cameras were in use, and the airport shows no signs of slowing down As of 2020, over 220 cameras were in use, and the airport shows no signs of slowing down. New projects will include building a fuel farm, a car wash and expanded parking facilities. XProtect’s open platform software As the need to increase security continues, XProtect’s open platform software will continue to enable both IT team growth and the seamless integration of new cameras and data storage capabilities. Solution - Integrations are in the fly zone Milestone XProtect Professional Plus and Smart Client Network cameras from Axis Communications and Panasonic Optimised video server hardware from Razberi Integrated video analytics from Agent Vi All video is stored for up to a full year, with most of the system’s 200 cameras set for motion recording, 24/7. Result - Greater situational awareness for higher security The video system has enabled improvements throughout the entire airport. For example, Jackson Hole Airport has to contend with a great deal of plane de-icing for several months each year. This occurs at a distance from the main buildings and, thanks to the video expansion, each airline is now able to monitor the de-icing of their planes. Allowing clients to monitor progress on their own has saved airport staff time and resources. The airport uses the system to closely monitor the security checkpoint, too, capturing video documentation in case of an incident. Baggage areas are also monitored, so it’s possible to investigate lost bags and left-behind items by reviewing video. New 4K, multi-sensor cameras New 4K, multi-sensor cameras support a largely unmanned investigatory system New 4K, multi-sensor cameras support a largely unmanned investigatory system. They capture everything and provide enough data to zoom in after the fact, if needed. Additionally, the team has deployed video analytics from Agent Vi to provide a layer of automated alarms and notifications for flagging abnormal occurrences. Video analytics can detect events, such as travelers moving against the foot traffic flow and crossing into restricted areas. Milestone’s XProtect Smart Client Milestone’s XProtect Smart Client has shifted general situational awareness in the airport, as a new standard for authorising users’ remote access to the surveillance from multiple locations. It provides seamless viewing of live and recorded video, instant control of cameras and connected security devices, and a comprehensive overview of activity. The ongoing use of Milestone Systems’ video management software (VMS) makes it possible to maintain the independence and efficiency of a small team of personnel, thereby delivering maximum security at the base of the Grand Teton Mountains. Situational awareness for the JAC team and their clients Andrew Wells, the IT Manager for the Jackson Hole Airport (JAC), said “Situational awareness for our team and our clients allows us to be as secure and efficient as possible with our small team. The flexibility of the open platform VMS allows us to scale our system and add the features we need now and in the future.” Jackson Hole Airport (JAC) lies seven miles north of Jackson, Wyoming, at the base of the Teton Mountains, in USA. It is unique for being entirely within Grand Teton National Park. It is the busiest airport in the US state of Wyoming, with nearly 500,000 in-bound passengers annually. The airport covers over 500 acres and has one runway that supports 11 hard-stands, nine boarding gates and three baggage carousels.


Round table discussion
While technology like cameras, alarms, and access control systems are crucial components, they are only as effective as the people who use and manage them and the systems that deploy them. When installing physical security systems, the focus should be on the holistic operation of the system rather than the functioning of individual components. However, in the end, overlooking critical factors can undermine the totality of system performance. We asked this week's Expert Panel Roundtable: What is the most overlooked factor when installing physical security systems?
As physical security technologies become more complex, it is incumbent on the dealer/integrator to have the skills and expertise needed to ensure that a system operates smoothly. The value of integrators increasingly rests on the skill sets they bring to bear when installing a system. If the skills are missing, there is a problem. We asked this week’s Expert Panel Roundtable: What missing skills among security integrators can cause problems for customers?
The death of Michael Brown at the hands of police in Ferguson, Missouri, in August 2014, highlighted to the public, the importance of body-worn cameras. There was no bodycam footage of the Ferguson tragedy. Arguably, it would have shed additional light on the shooting. Since then, body cameras have become a tangible legacy of Ferguson, Missouri. Bodycam footage is seen as providing greater accountability and ensuring an impartial record that can support, or debunk, any claims of police misconduct. Body-worn cameras are also finding their way into broader usage, even including customer service applications. We asked this week’s Expert Panel Roundtable: How important will body-worn cameras be moving forward?