Leuze has integrated artificial intelligence (AI) into optical distance sensors, enhancing measurement accuracy for complex industrial applications.
The innovation increases precision without additional operational computing resources, utilizing a neural network to make improvements.
Challenges with Object Surfaces
Optical distance sensors employing time-of-flight (TOF) technology offer considerable usage advantages by enabling quick, contactless measurement of wide-ranging distances, remaining unaffected by ambient light, and providing real-time data. The sensors measure distance based on the time it takes light to reach an object and return, typically using laser or LED pulses.
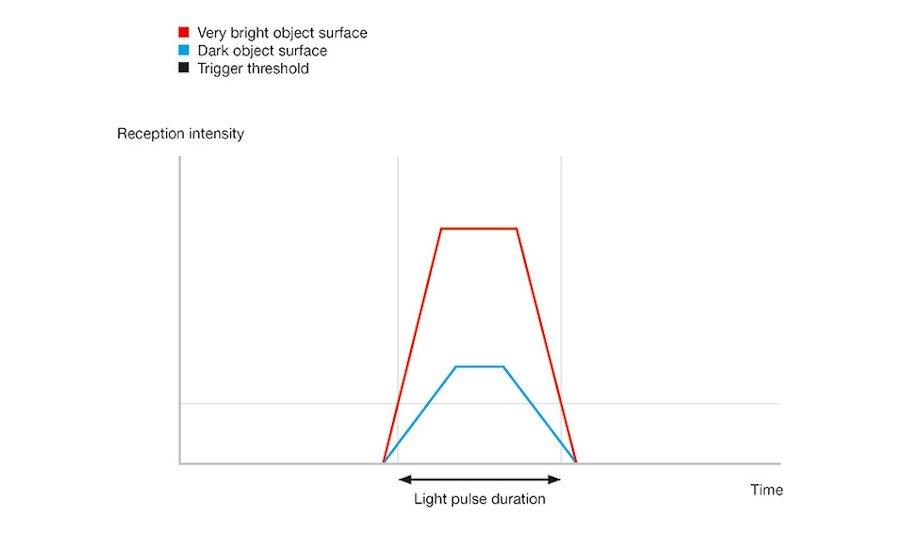
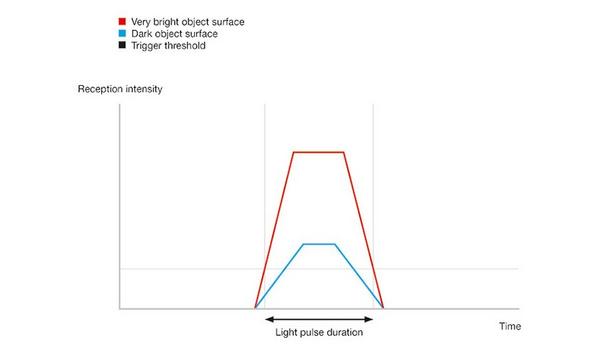
Despite these benefits, TOF technology faces accuracy limitations influenced by object surface characteristics. Dark surfaces may weaken the signal, causing delays as narrow pulses are detected later. Conversely, bright surfaces result in earlier, wider pulse detection, leading to measurement discrepancies that necessitate correction.
Polynomial Function Limitations
Traditionally, defined algorithms utilizing polynomial roles have been used for error correction
Traditionally, defined algorithms utilizing polynomial functions have been used for error correction.
These functions, while stable and suitable for continuous error curves, offer limited flexibility in managing complex surface reflections. As the parameters are fixed, they lack adaptability to changing environmental conditions.
Neural Networks for Enhanced Accuracy
Leuze has adopted a more advanced strategy with neural networks, a form of AI modeled on human brain functionality. The network comprises interconnected neurons across input, hidden, and output layers, processing input by passing through each layer sequentially.
This network design employs activation functions, enabling it to understand complex, non-linear scenarios beyond basic calculations.
Learning from Real Data
AI system developed by Leuze trains on sample data to understand how surface texture and brightness
The AI system developed by Leuze trains on sample data to understand how surface texture and brightness impact sensor readings. The neural network learns using raw distance values and pulse widths as inputs and standardized correction values as outputs.
This data originates during the production process, capturing information from varied surfaces and distances. The calculated correction values are then fed into the production system's neural network, requiring no additional computational effort from the sensor during actual operation.
Five-Step Precision Process
Leuze's neural network comprises five interconnected layers using a Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) activation function to filter out negative values. This configuration enhances speed and prevents computing errors typical of other approaches.
The network's final layer employs a hyperbolic tangent (tanh) function, ensuring that correction values stay within a set range, guiding sensor adjustments for accurate distance readings.
Applications in Industrial Automation
AI-enhanced time-of-flight sensors are invaluable in industrial automation where accuracy is critical. Notable applications include:
- Navigation and collision avoidance for robots and mobile platforms
- Material handling, ensuring precise positioning and distance checks on conveyors
- Quality assurance for distance checks on workpieces with challenging surfaces
- Automated guided vehicle systems (AGVs) for precise parking and maneuvering
- Safety applications involving proximity detection to machines and systems
Summary
With AI, Leuze elevates the precision of optical distance sensors, cutting measurement errors induced by surface and distance dependencies by more than half.
This AI-based correction provides more accurate and reliable measurements without extra operational effort, marking it as an effective solution for challenging industrial applications.
Key Advantages
- Significant reduction in measurement errors
- Versatile use across various sensor types and surfaces
- Enhanced learning from real data, adaptable to complex scenarios
- No additional computational burden during use
- Modern AI ensures future-proofing
Leuze uses artificial intelligence (AI) to significantly improve the measurement accuracy of optical distance sensors for challenging industrial applications.
This innovation improves measurement accuracy without the need for additional computing resources during operation. The solution is based on a neural network.
Object surfaces as challenges
Optical distance sensors with time-of-flight technology (TOF) offer practical benefits. The sensors enable fast, contactless measurement of large distances, are insensitive to ambient light and provide continuous distance data in real time. The sensor’s operating principle measure distances by recording the time it takes for emitted light to travel to the object and back. Laser or LED pulses are generally used for this purpose.
However, time-of-flight technology also has limitations in measurement accuracy: How precise the results are depends heavily on the nature of the object surface. Dark surfaces can weaken the reflected signal. They generate narrower pulses and the echo is detected later. Bright surfaces, on the other hand, generate stronger signals with a wider pulse width that are detected earlier. That means the returning signal is detected at different times depending on whether the object’s surface is light or dark. This can cause measurement errors that must be compensated for.
Polynomial function: Limited flexibility
Until now, mathematical models based on defined algorithms have been used to correct these errors. A correction value is calculated for many different surfaces and distances, which is later applied automatically. This calculation is based on a so-called polynomial function.
Polynomial functions offer an efficient solution for stable, continuous error curves. One disadvantage, however, is the limited imaging accuracy in the case of complex factors, such as strongly varying surface reflections. As the model parameters are fixed, the functions cannot automatically adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Neural network for correction value calculations
Leuze have a much more precise and flexible solution. Instead of working with rigid formulas, Leuze uses a neural network to determine the correction value. A neural network is a form of artificial intelligence that is modeled on the human brain. It consists of nodes (neurons) in three types of layers: the input layer, hidden layers and the output layer.
The neural network processes information by passing input data step through these one layer at a time. The neurons weigh their results, summarize them and convert them using functions so that a precise result is produced at the end. A so-called activation function decides how strongly a neuron becomes ‘active’, i.e. what value it passes on to the next layer. This activation function enables the network to learn even complex, non-linear relationships and is not limited to simple calculation patterns.
Learning from real data
The AI solution developed by Leuze uses sample data to learn how brightness and surface texture affect the optical distance sensor’s measurements. This makes it much easier to correct the measured values. The neural network is trained with data consisting of raw distance values and pulse widths as input parameters as well as the corresponding standardized correction values at the output.
The training data can be generated from the production process, in which many measured values are collected: for light, dark and differently textured surfaces as well as for different distances. These measured values are communicated to the production facility’s control system. From this, the production facility’s neural network calculates the correction values for the sensor. The sensor then requires no additional computing power during operation – the AI has already ‘learned’ everything.
Five steps for precise values
The Leuze neural network consists of five layers. In each layer, all neurons are fully connected to each other. This means that all information flows into the calculation. A so-called ReLU activation function is used: ReLU stands for ‘Rectified Linear Unit’. This ensures that the network sets negative counters to zero and only processes positive values – similar to a filter that only lets positive signals through, making the learning process stable and reliable.
This has two advantages: Firstly, the network works faster, and secondly, it avoids the computing problems that can occur with other methods. The last layer of the network – the output layer – determines the final correction value. Here, ‘tanh’ (hyperbolic tangent) is used as the activation function. This ensures that the calculated correction value is always within a defined range between -1 and +1. The system then converts this value so that it directly indicates how much the sensor must correct the measured distance in order to deliver precise results.
Calibrated to Leuze sensors
Time-of-flight distance sensors with AI-based correction are particularly useful in industrial automation where precise measurement results are essential.
Typical applications include:
- Navigation and collision avoidance: On robots and mobile platforms
- Materials handling: Checking positions and distances on conveyor belts
- Quality assurance: Checking distances on workpieces with difficult surfaces
- Automated guided vehicle systems (AGVs): Precise distance control when parking and maneuvering
- Safety applications: Detection of proximity to machines and systems
Summary
Leuze is raising the precision of optical distance sensors to a new level with artificial intelligence. Tests have shown that the method's AI-based calibration reduces systematic measurement errors, i.e. the dependence of measurement results on surface and distance, by more than half.
Customers benefit from more robust and accurate measurements without any effort during operation, even with difficult surfaces. This makes it the ideal solution for challenging industrial applications.
Benefits at a glance:
- Fewer measurement errors – delivering significantly more precise results
- Flexible use with different sensor types and surfaces
- Learns better from real data, even with strongly oscillating 3D curve characteristics
- No additional computing load during operation
- Future-proof thanks to modern AI